The recommended daily dose contains:
- Nicotinamide (Vitamin B3) 50,000 mg
- Thiamine nitrate (vitamin B1) 5,000 mg
- Pyridoxine Hydrochloride 4,000 mg
- Riboflavin (Vitamin B2) 1,000 mg
Nicotinamide (Vitamin B3)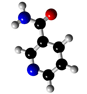
Nicotinamide (Vitamin B3) helps, together with other B vitamins, for the smooth functioning of the metabolism. It is important for skin, nerves and cell nuclei. Vitamin B3 gives more endurance during training, more energy and helps muscle growth. The body can obtain the vitamin through food or produce it from the amino acid tryptophan. Vitamin B3 is stored in the liver, so supplies usually last four to six weeks. However, a lack can occur as a result of an unbalanced diet or illness. Sunburn-like skin changes, diarrhea and loss of concentration may be the first signs of this. A balanced diet that contains all B vitamins is recommended. With dietary supplements containing vitamin B3, you can also compensate for any deficiency. B vitamins are known as "brain food". Almost all of them are soluble in water and for this reason must be taken constantly, as they do not stay in the body.
|
Thiamine nitrate (vitamin B1)
Vitamin B1 plays an important role in the proper functioning of muscles and nerves. Like other B vitamins, it also participates in cellular metabolic processes. It helps the body as a coenzyme to get energy from carbohydrates and fats and thus affects memory performance. Poor memory or fatigue may be a sign of a lack of vitamin B1, of which the human body can only accumulate small reserves. Heavy physical exertion can increase the likelihood of a deficiency of this vitamin, because carbohydrate metabolism is enhanced. Although a slight deficiency of vitamin B1 often occurs in developed countries, in practice the disease "beri-beri" has already disappeared. It is caused by an acute deficiency of vitamin B1 and seriously damages the nerves and muscles. Cereals contain a lot of vitamin B1. However, hulled beans are usually used for food production. The coats of seeds and sprouts with their high vitamin B1 content are lost during peeling. For a better supply of vitamin B1, it is good to include legumes such as lentils or soybeans in the menu. Pork and liver also contain large amounts of vitamin B1. Widespread vitamin B1 deficiency can be prevented with appropriate nutritional supplementation. This vitamin is essential for the metabolism of carbohydrates, for the flow of nerve impulses and for the normal functioning of muscles, and is also involved in the construction of nerve tissue.
|
Pyridoxine Hydrochloride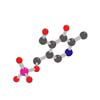
The body needs Pyridoxine Hydrochloride (Vitamin B6) to convert amino acids from food into its own proteins. Vitamin B6 thus makes an important contribution to metabolism. In addition, vitamin B6 is involved in the development of red blood cells, which supply the body with oxygen. Even the immune and nervous systems are affected by vitamin B6. For example, vitamin B6 is necessary for the formation of the "hormone of happiness" serotonin.
Fatigue, insomnia and nervousness can be symptoms of a weakening of the nervous system, which is based on the lack of vitamin B6. Even with a strong immune defense, vitamin B6 deficiency can have a negative impact. Changes or inflammation of the oral mucosa or the corners of the mouth may occur. Vitamin B6 is found in relatively many foods - especially meat, whole grains, potatoes, various vegetables, bananas and avocados. Nevertheless, a mild deficiency is not uncommon. A particularly protein-rich diet increases the need for vitamin B6.
Preparations containing vitamin B6 can easily supplement the daily nutritional intake. This vitamin is responsible for the normal content of magnesium in the body, brain activity and muscle activity. It is also necessary for the formation of red blood cells.
|
Riboflavin (Vitamin B2)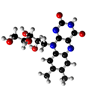
Vitamin B2 plays a central role in metabolism. It supports the conversion of carbohydrates, proteins and fats into energy. Vitamin B2 also plays an important role in the conversion of nutrients into fatty acids and endogenous proteins. It also supports the function of vitamins B6 and niacin (B3). Also known as riboflavin or vitamin B2 lactoflavin, it is mostly found in dairy products. But meat, wholemeal bread and some mushrooms are also good sources of vitamin B2. In cultures where corn is one of the staple foods, vitamin B2 deficiency occurs because corn is poor in it. Inflammation of the oral mucosa, cracked corners of the mouth or growth problems may be signs of vitamin B2 deficiency. In this case, the diet can be supplemented with appropriate preparations. This vitamin is responsible for the normal growth of the body and for supplying the cells with energy.
|




There are no reviews yet.